Eastman Kodak ASM-N-4 Dove
In April 1944, a Naval version of the U.S. Army Air Force's VB-6 Felix guided vertical bomb was approved, and the project was named Dove. Development was transferred to Eastman Kodak in July 1946, and the Dove was subsequently designated as air-to-surface guided missile ASM-4 (September 1947) and finally ASM-N-4 (early 1948). Development of the weapon's infrared guidance device apparently took some time, and it was not before 1949 that a contract for 20 XASM-N-4 prototypes was awarded.
 |
| Photo: via Ordway/Wakeford |
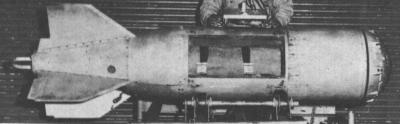
| XASM-N-4 |
The XASM-N-4 was basically a standard AN-M65 450 kg (1000 lb) general-purpose free-fall bomb, which was fitted with a simple heat-seeking device in the nose and control fins in the tail. The Dove could be dropped from unusually high (for a free-fall bomb) altitudes of up to 9100 m (30000 ft), because the seeker could correct aiming errors of up to 400 m (1/4 mile). Because it didn't use any significant lift devices, the XASM-N-4 was effectively a vertical bomb with no significant standoff range. The bomb was to be used against targets with a clear infrared signature, like ships in the open sea or isolated industrial plants.
Testing of the XASM-N-4 prototypes by the Bureau of Ordnance was completed in October 1952, but no follow-on production orders were placed.
Specifications
Note: Data given by several sources show slight variations. Figures given below may therefore be inaccurate!
Data for XASM-N-4:
| Length | 2.51 m (8 ft 3 in) |
| Finspan | 57.4 cm (22.6 in) |
| Diameter | 47.6 cm (18.8 in) |
| Weight | 610 kg (1350 lb) |
| Speed | Mach 0.98 |
| Propulsion | none |
| Warhead | 450 kg (1000 lb) AN-M65 general-purpose bomb |
Main Sources
[1] Norman Friedman: "US Naval Weapons", Conway Maritime Press, 1983
[2] Frederick I. Ordway III, Ronald C. Wakeford: "International Missile and Spacecraft Guide", McGraw-Hill, 1960
[3] Bill Gunston: "The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Rockets and Missiles", Salamander Books Ltd, 1979
Back to Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles, Appendix 1
Last Updated: 22 January 2003